The Enduring Legacy Of Ancient Egyptian Jewelry: A Journey Through Time And Style
The Enduring Legacy of Ancient Egyptian Jewelry: A Journey Through Time and Style
Related Articles: The Enduring Legacy of Ancient Egyptian Jewelry: A Journey Through Time and Style
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Enduring Legacy of Ancient Egyptian Jewelry: A Journey Through Time and Style. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Enduring Legacy of Ancient Egyptian Jewelry: A Journey Through Time and Style

Ancient Egyptian jewelry stands as a testament to the artistry and cultural significance of a civilization that flourished for millennia. Beyond mere ornamentation, these pieces served as powerful symbols of status, religious beliefs, and personal identity. This article delves into the rich history, intricate craftsmanship, and enduring appeal of ancient Egyptian jewelry, exploring its diverse forms, materials, and the profound meaning they held for the Egyptians.
A Tapestry of Time: Tracing the Evolution of Ancient Egyptian Jewelry
The evolution of Egyptian jewelry mirrors the changing fortunes of the civilization itself. From the predynastic period (c. 6000-3150 BCE) to the Ptolemaic era (305-30 BCE), jewelry design underwent significant transformations, reflecting evolving social, religious, and technological advancements.
Predynastic and Early Dynastic Periods (c. 6000-2686 BCE):
The earliest forms of jewelry emerged during the predynastic period, crafted from simple materials like bone, shell, and stone. These rudimentary pieces, often featuring geometric designs and animal motifs, served primarily as adornment and were likely worn by both men and women.
The Early Dynastic period (c. 3150-2686 BCE) witnessed the emergence of more sophisticated techniques and materials. Copper and gold were introduced, enabling the creation of intricate amulets and pendants. This period also saw the rise of the scarab beetle, a symbol of rebirth and transformation, becoming a prevalent motif in jewelry.
Old Kingdom (c. 2686-2181 BCE):
The Old Kingdom was a period of prosperity and artistic brilliance, reflected in the grandeur of the pyramids and the exquisite craftsmanship of its jewelry. Gold became the dominant material, employed in elaborate necklaces, bracelets, anklets, and rings. These pieces often featured intricate designs, including hieroglyphs, floral patterns, and representations of deities.
Middle Kingdom (c. 2055-1650 BCE):
The Middle Kingdom witnessed a shift in artistic style, with a greater emphasis on realism and naturalism. Jewelry continued to be crafted from gold, silver, and precious stones, but designs became more intricate and detailed. This period saw the introduction of faience, a glazed ceramic, which was widely used in the creation of amulets and beads.
New Kingdom (c. 1550-1070 BCE):
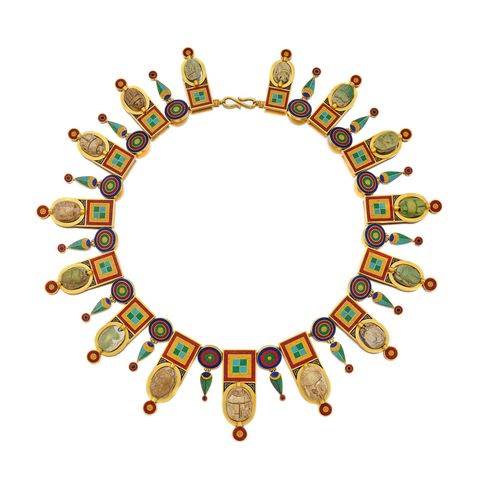
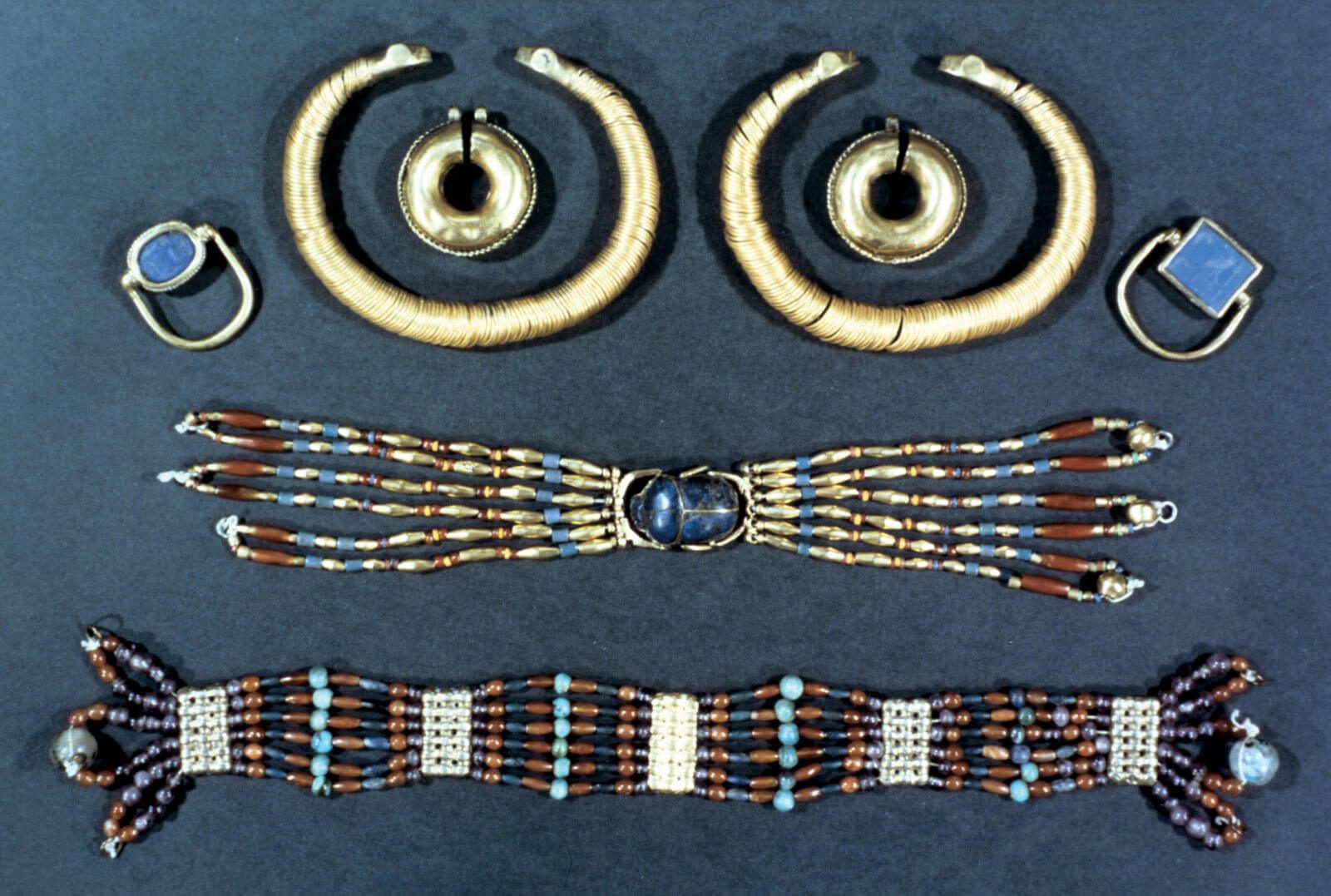
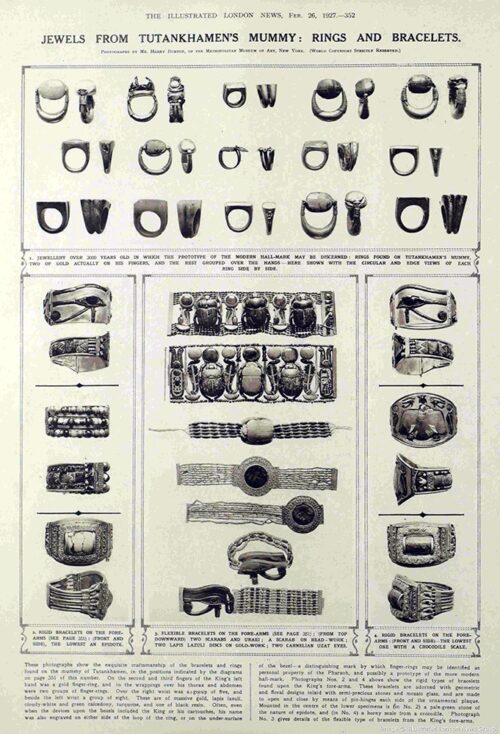
The New Kingdom, a period of Egyptian expansion and imperial power, is renowned for its opulent and elaborate jewelry. Gold, silver, lapis lazuli, turquoise, carnelian, and other precious stones were lavishly employed in necklaces, earrings, rings, and bracelets, often featuring intricate designs inspired by Egyptian mythology and religious beliefs.
Late Period and Ptolemaic Era (c. 664 BCE-30 BCE):
The Late Period and Ptolemaic era saw a decline in the quality and sophistication of Egyptian jewelry. The influence of foreign cultures, particularly Greek and Roman, became increasingly evident in the designs. While gold remained a popular material, cheaper metals like bronze and silver were also employed.
The Materials of Ancient Egyptian Jewelry: A Symphony of Nature and Craft
Ancient Egyptian jewelers were masters of their craft, employing a diverse array of materials to create stunning and enduring works of art. The most prized materials included:
- Gold: The primary material for Egyptian jewelry, gold symbolized wealth, power, and immortality. Its malleability allowed for intricate designs and delicate details.
- Silver: While less common than gold, silver was also used in jewelry, often in combination with gold to create contrasting effects.
- Precious Stones: A wide range of precious stones, including lapis lazuli, turquoise, carnelian, amethyst, and emerald, adorned Egyptian jewelry. These stones held symbolic significance and were believed to possess protective and healing properties.
- Faience: A glazed ceramic, faience was widely used in amulets and beads. Its vibrant colors and durability made it a popular material for everyday jewelry.
- Glass: Glassmaking was a significant achievement of ancient Egyptian civilization. Glass beads and pendants, often imitating precious stones, were widely used in jewelry.
- Bone and Ivory: These materials were used in early jewelry, particularly in the predynastic and early dynastic periods. Bone and ivory were carved into intricate designs and often adorned with geometric patterns.
- Shell: Shell was another material used in early jewelry, often used for beads and pendants. Its natural beauty and durability made it a popular choice for adornment.
The Symbolic Language of Ancient Egyptian Jewelry: More Than Just Decoration
Ancient Egyptian jewelry was not merely decorative; it was imbued with deep symbolic meaning, serving as a visual language that communicated status, religious beliefs, and personal identity.
- Amulets: Amulets were small, protective charms worn to ward off evil spirits and ensure good fortune. They were often made of faience, glass, or precious stones and featured images of deities, symbols, or protective inscriptions.
- Scarabs: The scarab beetle, a symbol of rebirth and transformation, was a popular motif in Egyptian jewelry. Scarab amulets were believed to bring good luck, protection, and a successful afterlife.
- Hieroglyphs: Hieroglyphs, the ancient Egyptian writing system, were often incorporated into jewelry, serving as personal inscriptions, prayers, or protective spells.
- Deities: Images of deities, such as Horus, Ra, Isis, and Osiris, were frequently depicted in jewelry, representing the wearer’s faith and seeking their protection.
- Floral Motifs: Flowers, such as the lotus and papyrus, held symbolic significance in ancient Egyptian culture. They were often depicted in jewelry, representing beauty, fertility, and the cyclical nature of life.
- Geometric Designs: Geometric patterns, such as triangles, squares, and circles, were also prevalent in Egyptian jewelry. These designs often represented cosmic order, harmony, and balance.
The Enduring Appeal of Ancient Egyptian Jewelry: A Timeless Legacy
The enduring appeal of ancient Egyptian jewelry lies in its combination of intricate craftsmanship, symbolic meaning, and timeless beauty. These pieces offer a glimpse into the rich cultural heritage of a civilization that has captivated the imagination for centuries.
- Historical Significance: Ancient Egyptian jewelry provides invaluable insights into the social, religious, and cultural practices of this ancient civilization.
- Artistic Mastery: The intricate designs, delicate details, and use of precious materials demonstrate the artistic skill and ingenuity of ancient Egyptian jewelers.
- Symbolic Depth: The symbolic meaning imbued in each piece adds a layer of depth and meaning to the jewelry, making it more than just ornamentation.
- Aesthetic Beauty: The timeless elegance and enduring beauty of ancient Egyptian jewelry continue to captivate and inspire.
FAQs about Ancient Egyptian Jewelry
Q: What were the most common types of ancient Egyptian jewelry?
A: The most common types of ancient Egyptian jewelry included necklaces, bracelets, anklets, rings, earrings, and amulets.
Q: What were the primary materials used in ancient Egyptian jewelry?
A: The primary materials used in ancient Egyptian jewelry included gold, silver, precious stones, faience, glass, bone, ivory, and shell.
Q: What was the significance of scarab beetles in ancient Egyptian jewelry?
A: Scarab beetles symbolized rebirth and transformation and were believed to bring good luck, protection, and a successful afterlife.
Q: What were hieroglyphs used for in ancient Egyptian jewelry?
A: Hieroglyphs were used as personal inscriptions, prayers, or protective spells in ancient Egyptian jewelry.
Q: What are some examples of deities depicted in ancient Egyptian jewelry?
A: Some examples of deities depicted in ancient Egyptian jewelry include Horus, Ra, Isis, and Osiris.
Q: What is the significance of floral motifs in ancient Egyptian jewelry?
A: Flowers, such as the lotus and papyrus, represented beauty, fertility, and the cyclical nature of life in ancient Egyptian culture.
Q: Why is ancient Egyptian jewelry still so popular today?
A: Ancient Egyptian jewelry remains popular today due to its historical significance, artistic mastery, symbolic depth, and aesthetic beauty.
Tips for Appreciating and Collecting Ancient Egyptian Jewelry
- Research: Learn about the different periods, materials, and styles of ancient Egyptian jewelry.
- Authenticity: Be cautious of fakes and replicas. Look for pieces with provenance and documentation.
- Quality: Examine the craftsmanship, materials, and condition of the jewelry.
- Significance: Consider the symbolic meaning and cultural context of the pieces you are interested in.
- Conservation: Handle ancient Egyptian jewelry with care and store it appropriately to preserve its integrity.
Conclusion: A Legacy That Endures
Ancient Egyptian jewelry stands as a testament to the artistry, cultural significance, and enduring legacy of a civilization that has captivated the world for millennia. From the intricate designs and precious materials to the profound symbolic meaning embedded in each piece, these works of art continue to inspire and captivate. As we delve into the history and artistry of ancient Egyptian jewelry, we gain a deeper understanding of the rich tapestry of human creativity and the enduring power of symbols and beauty.




![[Egyptian Jewelry: A Window into Ancient Culture] American Research](https://www.arce.org/sites/default/files/2019-02/21X_CAT115R1.jpg)
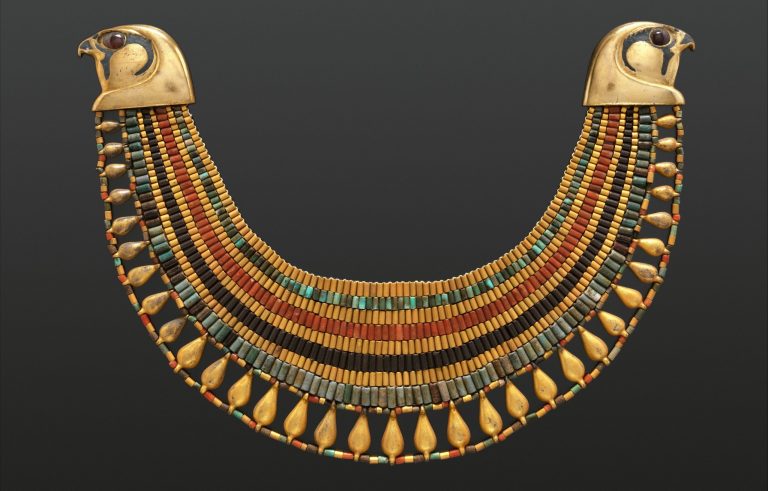


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Enduring Legacy of Ancient Egyptian Jewelry: A Journey Through Time and Style. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!