The Rise Of 3D Jewelry Printing: Shaping The Future Of Design And Creation
The Rise of 3D Jewelry Printing: Shaping the Future of Design and Creation
Related Articles: The Rise of 3D Jewelry Printing: Shaping the Future of Design and Creation
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Rise of 3D Jewelry Printing: Shaping the Future of Design and Creation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Rise of 3D Jewelry Printing: Shaping the Future of Design and Creation

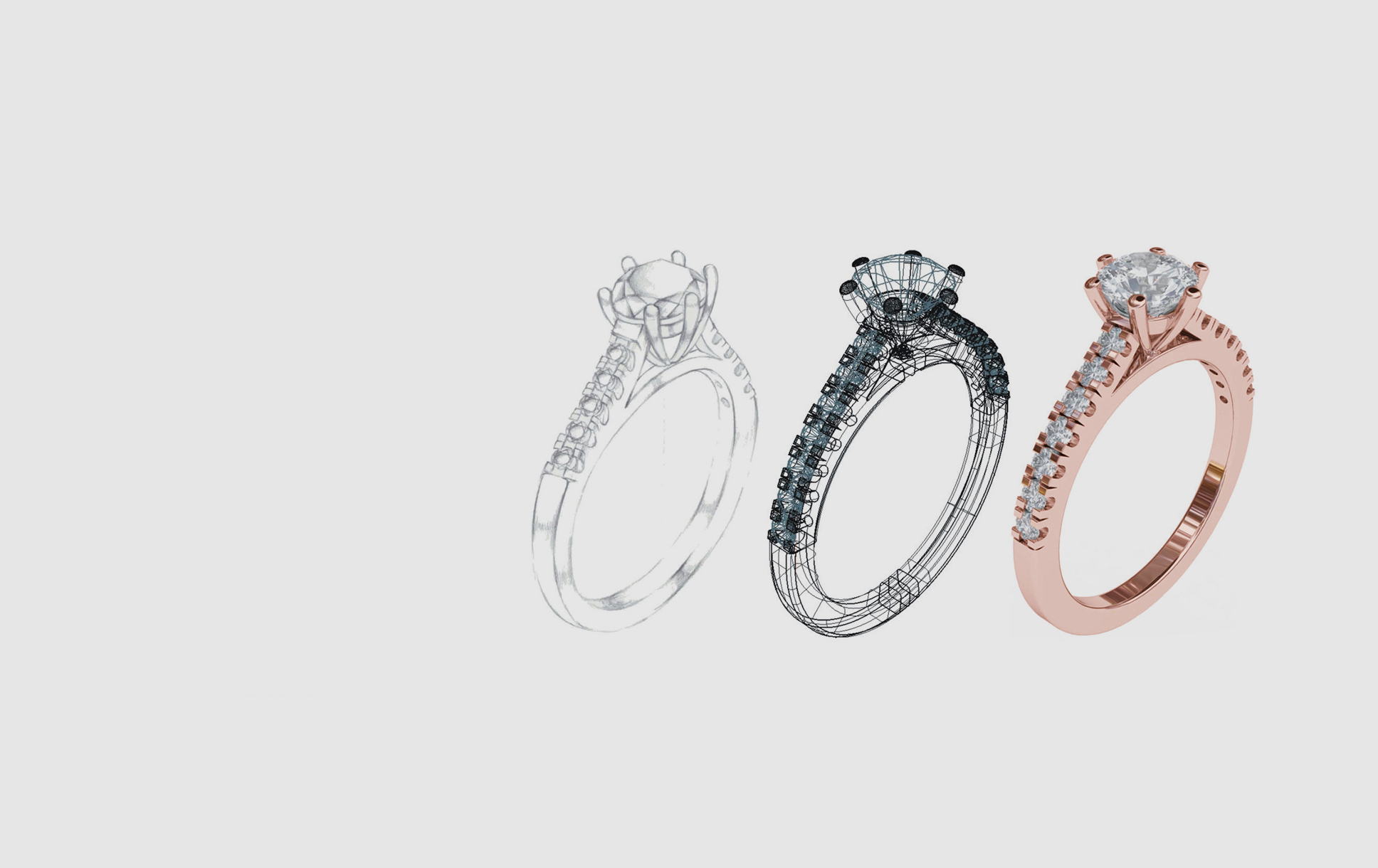
The world of jewelry design has undergone a significant transformation in recent years, propelled by the advent of 3D printing technology. This innovative approach to fabrication has revolutionized the way jewelry is conceived, designed, and produced, opening up a world of possibilities for both established jewelers and aspiring designers.
Understanding 3D Jewelry Printing: A Technological Revolution
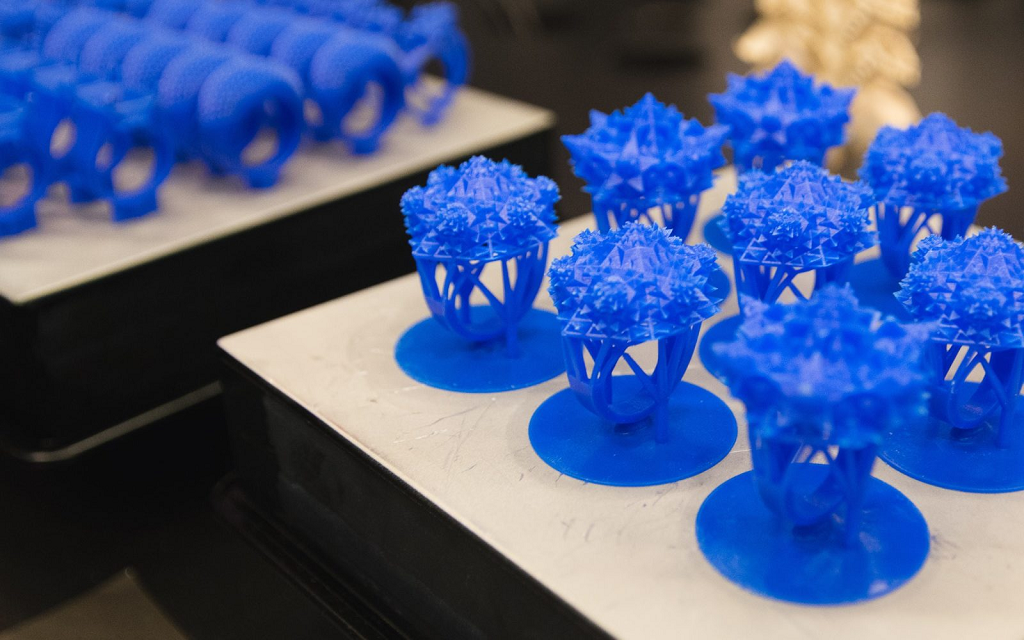
3D jewelry printing, also known as additive manufacturing, involves the construction of three-dimensional objects layer by layer from a digital model. This process utilizes a variety of materials, including wax, resin, precious metals, and even ceramics, to create intricate and highly detailed jewelry pieces.
Key Benefits of 3D Jewelry Printing:
-
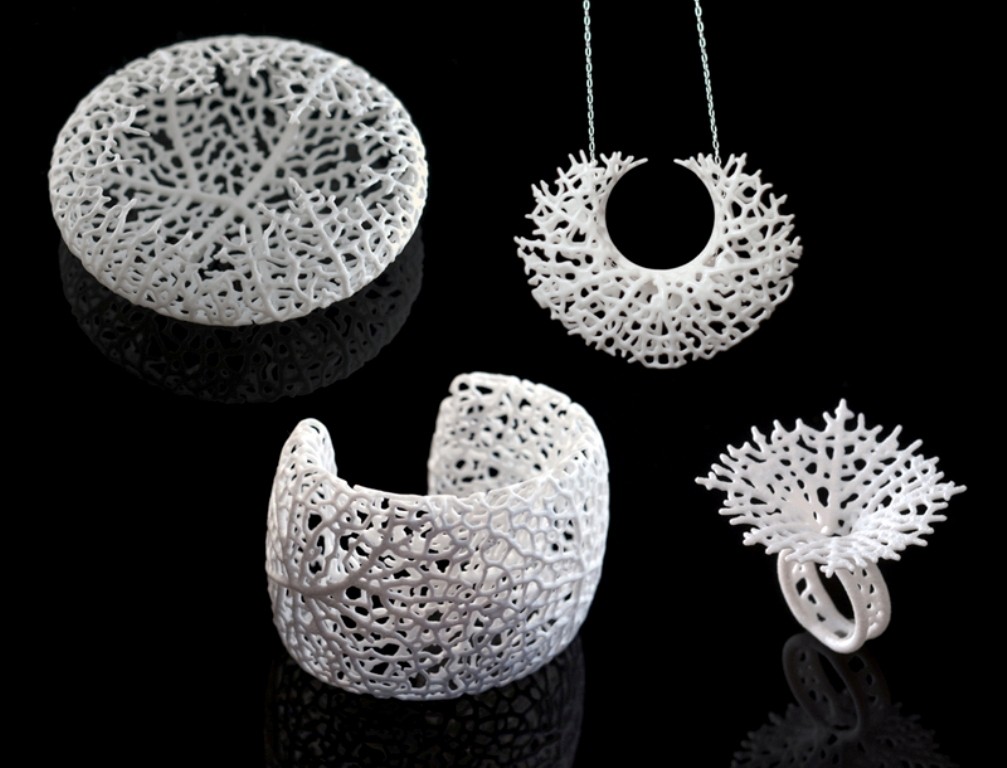
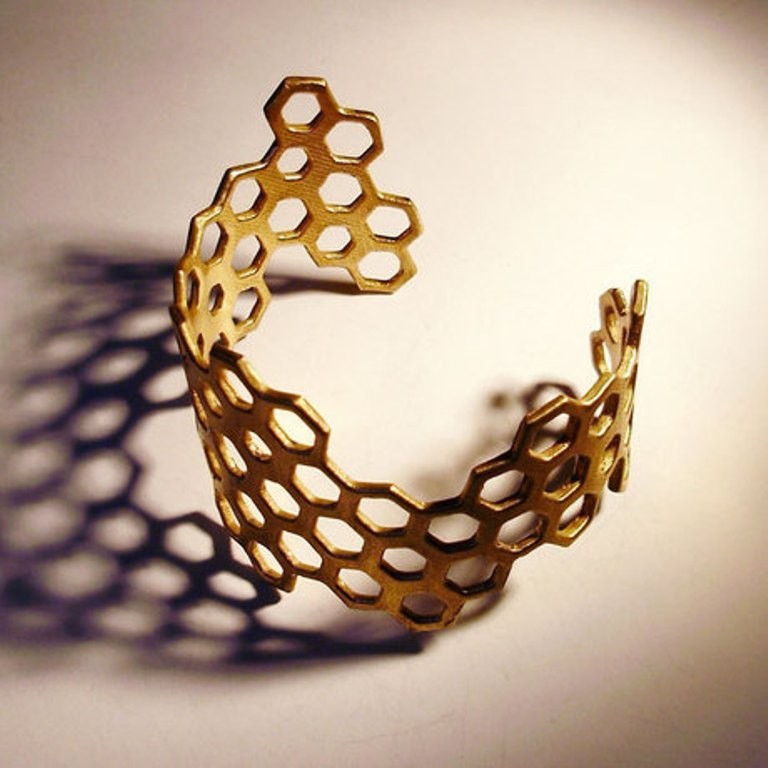
Unparalleled Design Flexibility: 3D printing empowers designers to break free from traditional constraints, allowing them to create intricate geometries, complex patterns, and personalized designs that would be impossible to achieve through conventional methods.
-
Rapid Prototyping and Customization: The ability to quickly translate digital designs into physical prototypes enables rapid iteration and refinement, accelerating the design process and facilitating personalized creations.
-
Cost-Effectiveness and Efficiency: 3D printing eliminates the need for expensive molds and casting processes, making it a cost-effective solution for small-batch production and customized jewelry.
-
Sustainable Manufacturing: 3D printing minimizes material waste and reduces the environmental impact associated with traditional jewelry production methods.
-
Expanding Material Options: The technology continually evolves, expanding the range of materials that can be used for jewelry printing, including precious metals, ceramics, and even biocompatible materials for medical jewelry.
Types of 3D Jewelry Printing Technologies:
-
Stereolithography (SLA): This process utilizes a vat of liquid photopolymer resin that is selectively cured by a UV laser, layer by layer, to create a solid object. SLA is known for its high resolution and detail, making it ideal for intricate designs and delicate pieces.
-
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): SLS involves using a laser to fuse powdered materials, such as nylon or metal, layer by layer, to create a solid object. SLS is known for its strength and durability, making it suitable for larger and more robust jewelry pieces.
-
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): FDM uses a thermoplastic filament that is extruded layer by layer through a heated nozzle, building up the object. FDM is a versatile and affordable technology, well-suited for prototyping and experimenting with different designs.
Applications of 3D Jewelry Printing:
-
Prototype Development: 3D printing enables designers to quickly create prototypes for new designs, allowing them to test different forms, textures, and materials before committing to production.
-
Personalized Jewelry: The technology facilitates the creation of unique and customized jewelry pieces, from personalized engravings to bespoke designs tailored to individual preferences.
-
Limited Edition Collections: 3D printing enables small-scale production runs, allowing jewelers to create exclusive and limited-edition collections for discerning customers.
-
Mass Customization: 3D printing can be used to create personalized jewelry on a larger scale, enabling retailers to offer a wide range of customizable options to their customers.
-
Fine Jewelry Production: The advancements in 3D printing technology have made it possible to create high-quality jewelry pieces using precious metals like gold and silver.
The Future of 3D Jewelry Printing:
The future of 3D jewelry printing holds immense promise for both designers and consumers. Continued advancements in technology are expected to lead to:
-
Enhanced Material Capabilities: New materials with unique properties and finishes will be developed, expanding the creative possibilities for jewelry designers.
-
Improved Printing Resolution: Higher resolution printing will allow for even more intricate details and realistic textures, pushing the boundaries of design complexity.
-
Increased Production Speed: Faster printing speeds will enable more efficient production processes, making 3D printing even more cost-effective for both small and large-scale jewelry production.
-
Integration with AI and Automation: The integration of artificial intelligence and automation will further streamline the design and production process, enabling more efficient and personalized jewelry creation.
Frequently Asked Questions about 3D Jewelry Printing:
Q: What materials can be used for 3D jewelry printing?
A: A wide range of materials can be used for 3D jewelry printing, including:
- Resins: Photopolymer resins offer a variety of colors and finishes, ideal for intricate designs.
- Wax: Wax is often used for lost wax casting, where a 3D printed wax model is used to create a mold for casting in precious metals.
- Metals: Precious metals like gold, silver, and platinum can be used for 3D printing, allowing for intricate designs and high-quality finishes.
- Ceramics: 3D printing with ceramics opens up new possibilities for unique and durable jewelry pieces.
- Biocompatible Materials: Biocompatible materials are being used for medical jewelry, such as implants and prosthetics.
Q: Is 3D printed jewelry durable?
A: The durability of 3D printed jewelry depends on the material used and the printing process. Some materials, like resins, may be more susceptible to scratching or chipping, while others, like metals, are highly durable.
Q: How much does 3D jewelry printing cost?
A: The cost of 3D jewelry printing varies depending on factors such as the material used, the complexity of the design, and the quantity being produced. However, 3D printing is generally more cost-effective than traditional jewelry production methods, especially for small-batch production and customized pieces.
Q: How do I care for 3D printed jewelry?
A: The care instructions for 3D printed jewelry vary depending on the material used. It’s important to consult the manufacturer’s guidelines for specific cleaning and storage recommendations.
Tips for Designing and Printing Jewelry with 3D Technology:
- Start with a Digital Model: Create a detailed digital model of your jewelry design using CAD software.
- Consider the Material: Choose the appropriate material for your design based on its intended use, durability requirements, and aesthetic preferences.
- Optimize for 3D Printing: Ensure your design is optimized for 3D printing by considering factors like overhangs, supports, and print orientation.
- Experiment with Prototypes: Create prototypes to test different designs, materials, and printing processes before committing to production.
- Choose a Reputable Printer: Select a reputable 3D printer manufacturer and service provider to ensure high-quality printing and reliable support.
Conclusion:
3D jewelry printing has emerged as a transformative force in the jewelry industry, empowering designers and consumers alike. The technology offers unparalleled design flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and a sustainable approach to production. As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative and personalized jewelry creations, pushing the boundaries of design and craftsmanship. The future of jewelry is being shaped by the power of 3D printing, and the possibilities are truly limitless.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Rise of 3D Jewelry Printing: Shaping the Future of Design and Creation. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!