The Rise Of 3D Printing In Jewelry: A Revolution In Design And Production
The Rise of 3D Printing in Jewelry: A Revolution in Design and Production
Related Articles: The Rise of 3D Printing in Jewelry: A Revolution in Design and Production
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Rise of 3D Printing in Jewelry: A Revolution in Design and Production. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Rise of 3D Printing in Jewelry: A Revolution in Design and Production
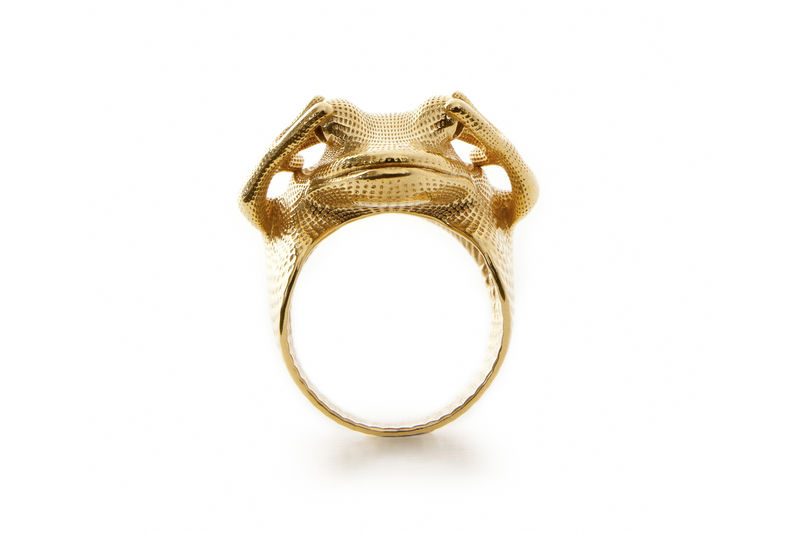

3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has emerged as a transformative technology in the jewelry industry, offering a unique blend of creative freedom, cost-effectiveness, and efficiency. By building objects layer by layer from digital designs, 3D printing allows jewelers to create intricate and complex pieces that were previously impossible or prohibitively expensive to manufacture using traditional methods. This article delves into the world of 3D printing machines for jewelry, exploring their capabilities, benefits, and applications in shaping the future of this age-old craft.
Understanding 3D Printing for Jewelry
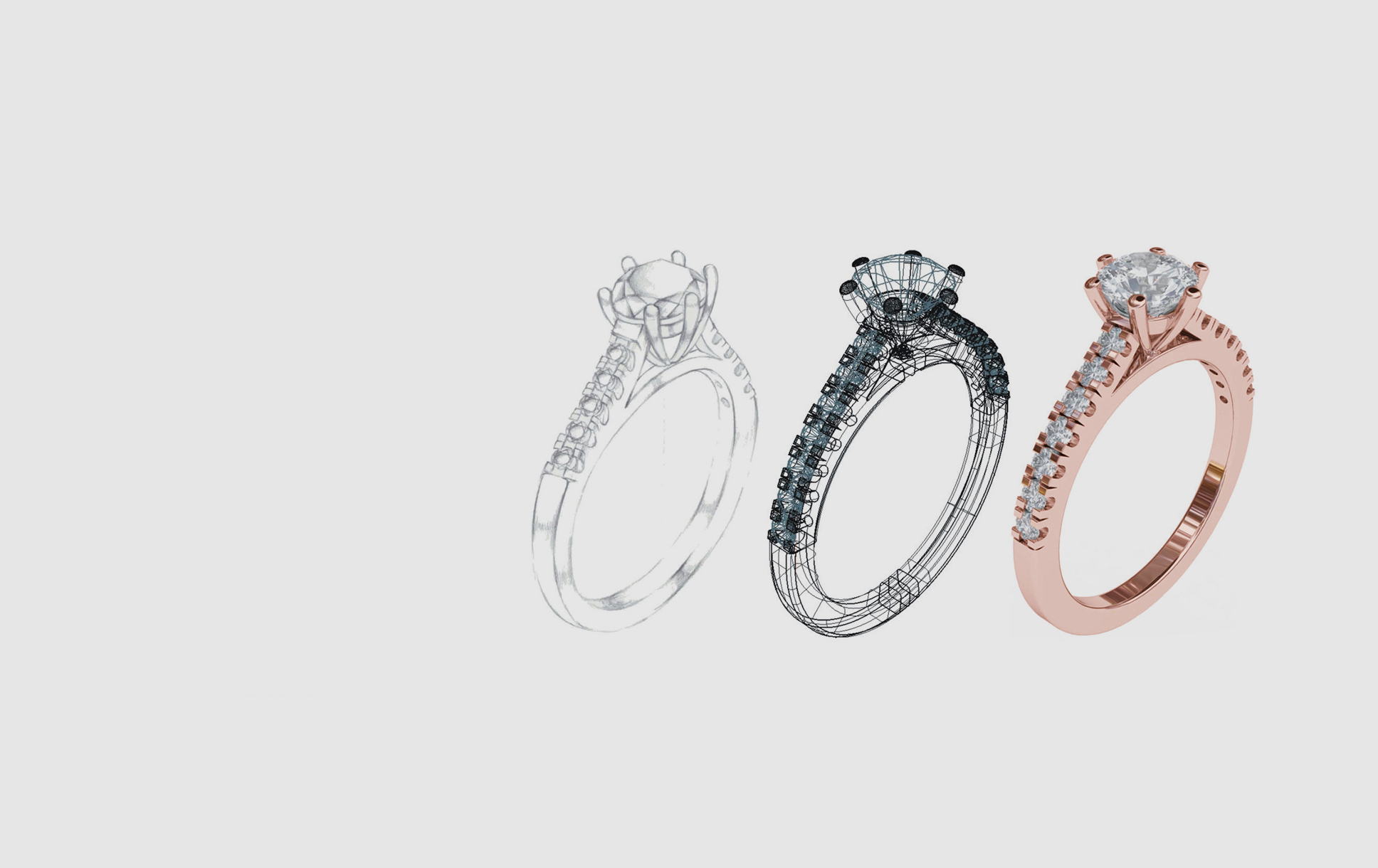
At its core, 3D printing for jewelry involves using a computer-aided design (CAD) software to create a digital model of the desired piece. This digital model is then translated into instructions for a 3D printer, which builds the object layer by layer, using a variety of materials, including wax, resin, and metal.
Types of 3D Printing Technologies for Jewelry
The jewelry industry utilizes several 3D printing technologies, each with its own strengths and limitations:
-
Stereolithography (SLA): SLA printers use a vat of liquid photopolymer resin that is cured by a UV laser, solidifying layer by layer to create the desired object. SLA is known for its high resolution and excellent surface finish, making it ideal for creating intricate and detailed jewelry pieces.
-
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): SLS printers use a laser to fuse powdered materials, such as nylon, metal, or ceramic, layer by layer. This process produces strong and durable pieces with excellent detail, making it suitable for creating rings, pendants, and other pieces requiring structural integrity.
-
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): FDM printers extrude molten plastic filament through a nozzle, building up the object layer by layer. FDM is a relatively affordable and accessible technology, making it popular for prototyping and small-scale jewelry production.
-
Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS): DMLS printers utilize a laser to fuse powdered metal, creating complex and intricate designs with excellent dimensional accuracy and high strength. DMLS is particularly well-suited for creating fine jewelry pieces, such as engagement rings and custom-made pieces.
-
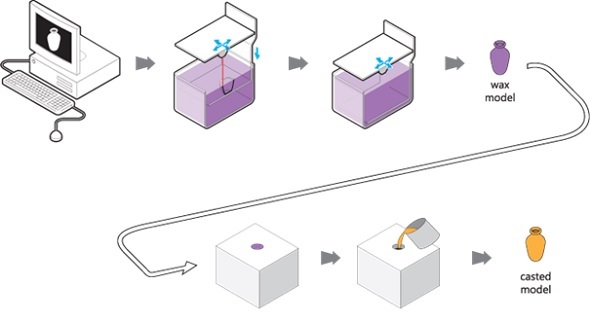
Lost Wax Casting: This technique involves using a 3D printed wax model as a mold for casting metal jewelry. The wax model is then heated and melted away, leaving a hollow mold that is filled with molten metal. This process allows for the creation of intricate and detailed jewelry pieces with a high degree of precision.
Benefits of 3D Printing for Jewelry
The adoption of 3D printing in the jewelry industry has brought about a paradigm shift, offering numerous advantages:
-
Design Freedom: 3D printing empowers jewelers to explore complex and unconventional designs, pushing the boundaries of traditional jewelry making. The ability to create intricate details, organic shapes, and personalized designs unlocks a world of creative possibilities.
-
Reduced Lead Times: 3D printing eliminates the need for traditional molds and casting processes, significantly reducing production time. This allows jewelers to create custom pieces and prototypes quickly, responding to customer demands with greater efficiency.
-
Cost-Effectiveness: 3D printing can be more cost-effective than traditional jewelry making, particularly for small-scale production runs and custom pieces. The elimination of tooling costs and the ability to create intricate designs without the need for elaborate molds contribute to reduced overall costs.
-
Increased Customization: 3D printing enables jewelers to personalize pieces for individual customers, creating unique and meaningful pieces that reflect their personal style and preferences. This level of customization caters to the growing demand for personalized and bespoke jewelry.
-
Sustainability: 3D printing offers a more sustainable approach to jewelry production. By reducing waste and minimizing material consumption, it contributes to a more environmentally friendly manufacturing process.
Applications of 3D Printing in Jewelry
3D printing has revolutionized various aspects of the jewelry industry, impacting design, production, and even retail:
-
Prototyping: 3D printing allows jewelers to rapidly create prototypes and test different designs before committing to costly production runs. This iterative process helps refine designs and ensures customer satisfaction.
-
Custom Jewelry: 3D printing enables the creation of personalized jewelry pieces, catering to individual preferences and style. From engagement rings to bespoke necklaces, 3D printing allows for a unique and personalized touch.
-
Fine Jewelry: 3D printing has become increasingly popular for creating high-end jewelry pieces, offering intricate details, complex shapes, and high-quality finishes.
-
Mass Customization: 3D printing facilitates mass customization, allowing jewelers to offer a wide range of personalized designs while maintaining affordability.
-
Production Efficiency: 3D printing streamlines production processes, reducing the time and cost associated with traditional jewelry making. This allows jewelers to scale their businesses and meet growing customer demands.
-
Retail Innovation: 3D printing has revolutionized retail, enabling jewelers to offer on-demand customization and personalized services. Customers can design their own jewelry pieces, and jewelers can create them instantly, providing a unique and engaging shopping experience.
Challenges of 3D Printing for Jewelry
While 3D printing offers numerous advantages, it also presents certain challenges:
-
Material Limitations: The range of materials available for 3D printing is still limited compared to traditional jewelry making. While advancements are being made, certain materials, such as precious metals, are not yet readily available for 3D printing.
-
Scale and Cost: 3D printing is not always cost-effective for large-scale production runs, particularly when compared to traditional manufacturing methods. The cost of 3D printers and materials can also be a barrier for some jewelers.
-
Skill and Expertise: Operating and maintaining 3D printers requires specific skills and knowledge. Jewelers need to be trained in CAD software and 3D printing techniques to effectively utilize this technology.
-
Post-Processing: 3D printed jewelry often requires post-processing steps, such as sanding, polishing, and finishing, to achieve the desired aesthetic and durability.
The Future of 3D Printing in Jewelry
The jewelry industry is on the cusp of a technological revolution driven by 3D printing. Continued advancements in materials, software, and printing technologies are expected to further enhance the capabilities and applications of 3D printing in jewelry making.
-
New Materials: Research and development are constantly expanding the range of materials suitable for 3D printing, including precious metals, ceramics, and composites. This will open up new possibilities for design and functionality.
-
Improved Resolution and Detail: Advancements in 3D printing technology are leading to higher resolutions and greater detail, enabling the creation of even more intricate and realistic jewelry pieces.
-
Software Integration: Software advancements are streamlining the design and production processes, enabling greater automation and integration between CAD software and 3D printing machines.
-
Mass Adoption: As the cost of 3D printing technology continues to decrease and the benefits become more apparent, we can expect to see wider adoption across the jewelry industry, leading to increased innovation and accessibility.
FAQs
1. What is the cost of a 3D printer for jewelry?
The cost of a 3D printer for jewelry can vary significantly depending on the technology, size, and features. Entry-level FDM printers can be purchased for a few hundred dollars, while professional-grade SLA and DMLS printers can cost tens of thousands of dollars.
2. What materials can be used for 3D printing jewelry?
3D printing for jewelry utilizes a variety of materials, including:
- Wax: Used for lost wax casting, wax models are melted away, leaving a hollow mold for casting metal jewelry.
- Resin: Photopolymer resins offer high resolution and excellent surface finish, making them ideal for intricate and detailed jewelry pieces.
- Metal: Metal powders are used in DMLS and other processes to create strong and durable jewelry pieces.
- Plastic: FDM printers use plastic filaments to create prototypes and affordable jewelry pieces.
3. How long does it take to 3D print a jewelry piece?
The printing time for a jewelry piece depends on the size, complexity, and material used. Simple pieces can be printed in a few hours, while intricate designs can take several days.
4. What are the advantages of 3D printing over traditional jewelry making?
3D printing offers numerous advantages over traditional jewelry making, including:
- Design freedom
- Reduced lead times
- Cost-effectiveness
- Increased customization
- Sustainability
5. What are the limitations of 3D printing for jewelry?
The limitations of 3D printing for jewelry include:
- Material limitations
- Scale and cost
- Skill and expertise
- Post-processing requirements
Tips for Using a 3D Printer for Jewelry
- Invest in quality CAD software: Choose a CAD software that is specifically designed for jewelry making and offers a wide range of tools and features.
- Learn 3D printing techniques: Take courses or workshops to learn the basics of 3D printing, including design, slicing, and printing.
- Experiment with different materials: Explore the different materials available for 3D printing and choose the best option for your project.
- Invest in post-processing tools: Ensure you have the necessary tools for sanding, polishing, and finishing 3D printed jewelry.
- Stay informed about industry trends: Keep up with the latest advancements in 3D printing technology and materials to stay competitive.
Conclusion
3D printing has revolutionized the jewelry industry, offering a blend of creative freedom, cost-effectiveness, and efficiency. From prototyping to custom jewelry and mass customization, 3D printing has become an integral part of the modern jewelry landscape. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative applications of 3D printing in jewelry making, pushing the boundaries of design and production and shaping the future of this age-old craft.
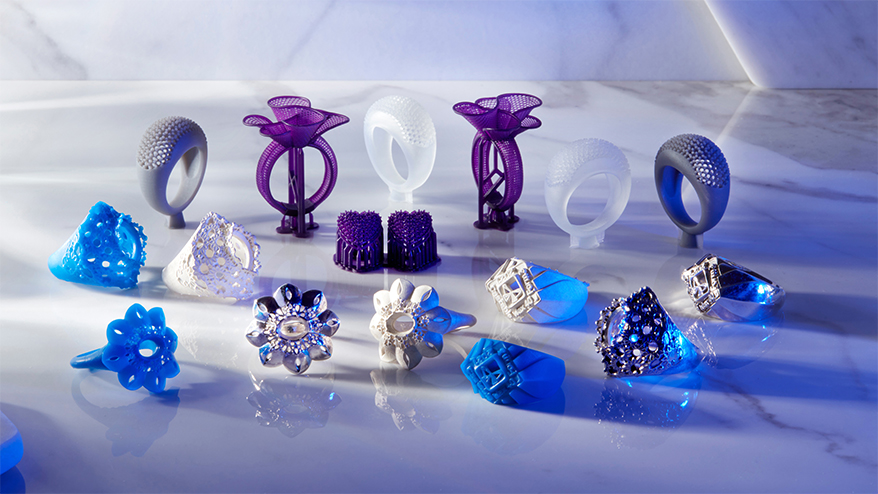
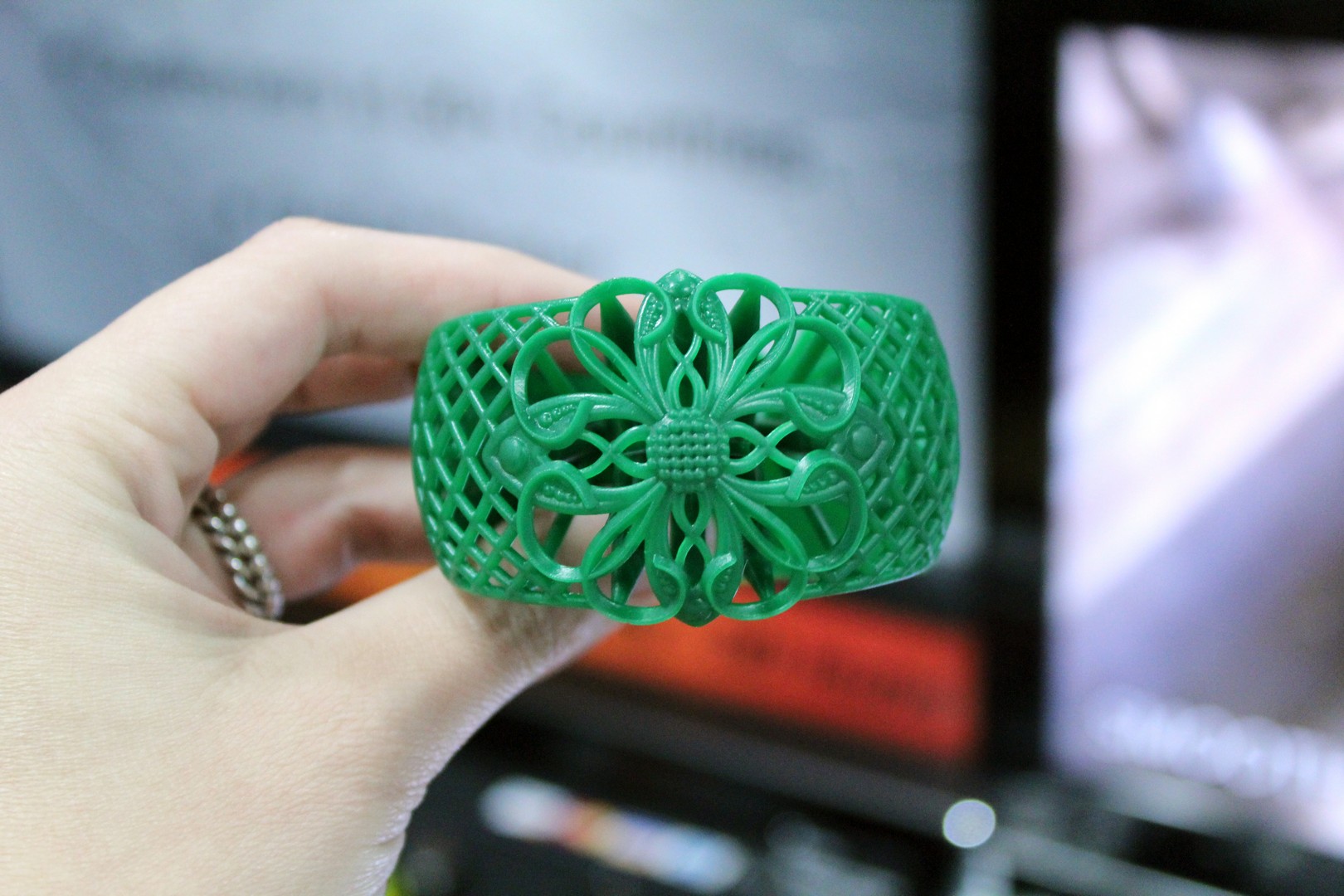







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Rise of 3D Printing in Jewelry: A Revolution in Design and Production. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!