The Rise Of 3D Printing In Jewelry: A Revolution In Design And Production
The Rise of 3D Printing in Jewelry: A Revolution in Design and Production
Related Articles: The Rise of 3D Printing in Jewelry: A Revolution in Design and Production
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Rise of 3D Printing in Jewelry: A Revolution in Design and Production. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Rise of 3D Printing in Jewelry: A Revolution in Design and Production
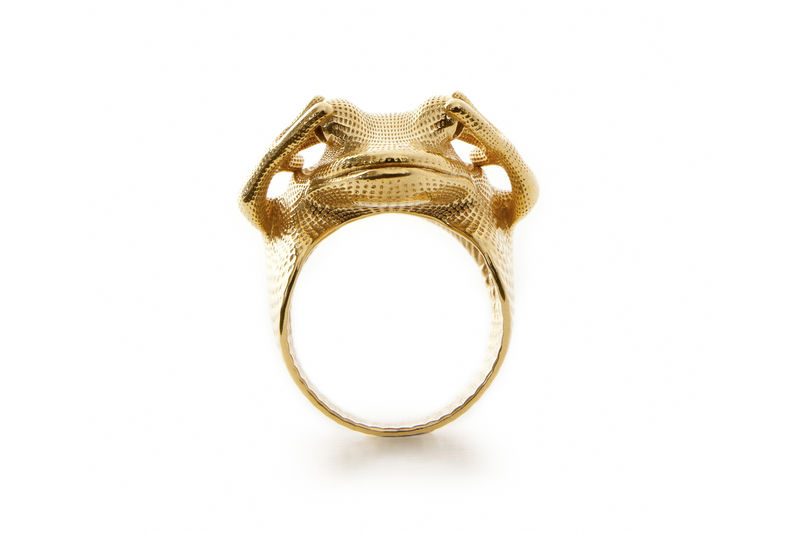

The jewelry industry, traditionally rooted in craftsmanship and intricate manual processes, is undergoing a significant transformation. At the forefront of this revolution is 3D printing, a technology that is rapidly changing how jewelry is designed, produced, and consumed. This article delves into the intricacies of 3D jewelry printing, exploring its potential, benefits, and the impact it is having on the jewelry landscape.
Understanding 3D Jewelry Printing: A Technological Breakthrough
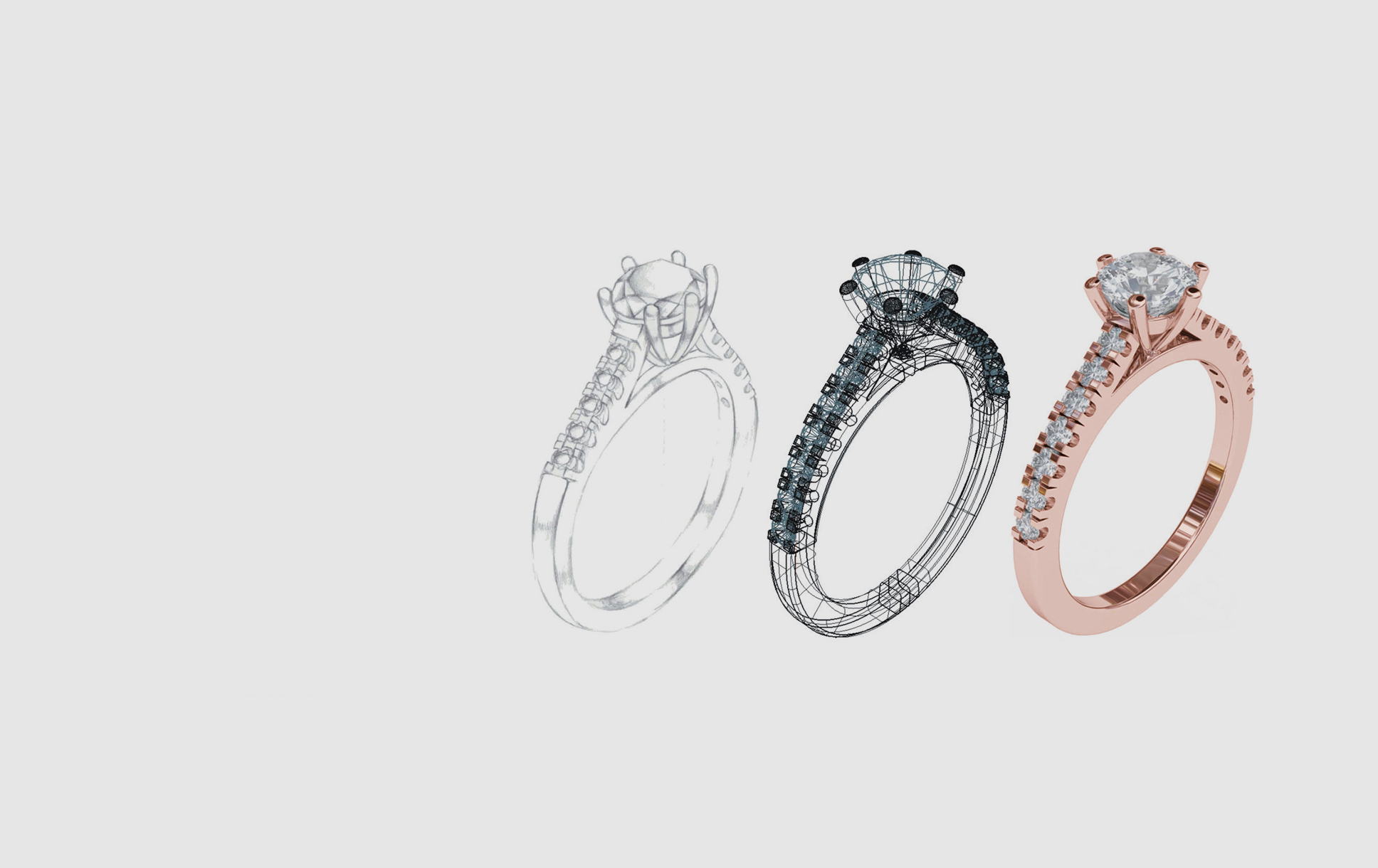
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, utilizes a digital design to create a three-dimensional object layer by layer. The process involves feeding a computer-aided design (CAD) file into a 3D printer, which then uses specialized materials, such as wax, resin, or metal, to build the object. In the context of jewelry, 3D printing offers a remarkable level of precision and detail, allowing for the creation of intricate designs that would be impossible to achieve through traditional methods.
The Advantages of 3D Jewelry Printing: Shaping the Future of Jewelry
The adoption of 3D printing in the jewelry industry brings forth numerous advantages, revolutionizing the design, production, and distribution of jewelry.
1. Unparalleled Design Freedom:
3D printing empowers jewelry designers to break free from the limitations of traditional techniques. Complex geometries, intricate patterns, and personalized designs become readily achievable, fostering a new era of creativity and artistic expression. Designers can experiment with unique shapes, textures, and styles, creating pieces that are truly one-of-a-kind.
2. Customization and Personalization:
3D printing facilitates the production of highly personalized jewelry. Customers can collaborate with designers to create pieces tailored to their specific preferences, incorporating personal details like names, initials, dates, or even intricate symbols. This ability to customize jewelry caters to individual tastes and allows for the creation of truly meaningful and unique pieces.
3. Rapid Prototyping and Reduced Lead Times:
The rapid prototyping capabilities of 3D printing significantly shorten the design and production cycle. Designers can quickly iterate and refine their designs, creating multiple prototypes within a short timeframe. This agility enables faster turnaround times, allowing for quicker product development and faster delivery to customers.
4. Reduced Material Waste and Cost Efficiency:
3D printing is an inherently efficient process, minimizing material waste compared to traditional techniques. The additive nature of the process allows for the precise use of materials, reducing unnecessary material consumption and minimizing environmental impact. Additionally, the efficiency of 3D printing translates into cost savings, making jewelry more accessible to a wider range of consumers.
5. Enhanced Detail and Precision:
3D printing offers unparalleled precision and detail in jewelry production. The layered approach allows for the creation of intricate designs with fine details, textures, and patterns that would be difficult or impossible to achieve through traditional methods. This level of precision elevates the aesthetic appeal of jewelry, creating pieces that are visually stunning and captivating.
6. Production Flexibility and Scalability:
3D printing provides immense flexibility and scalability in jewelry production. It allows for the production of both small batches of bespoke pieces and large-scale production runs, catering to diverse market needs. This flexibility enables designers and manufacturers to adapt to changing trends and customer demands, ensuring a continuous flow of innovative and desirable jewelry.
7. Accessibility and Democratization of Jewelry:
3D printing opens up new avenues for jewelry production, making it more accessible to independent designers and small businesses. The technology lowers the barriers to entry, enabling individuals with creative vision to establish their own jewelry lines without the need for large-scale investments in traditional manufacturing equipment. This democratization fosters innovation and competition, enriching the jewelry landscape with diverse perspectives and styles.
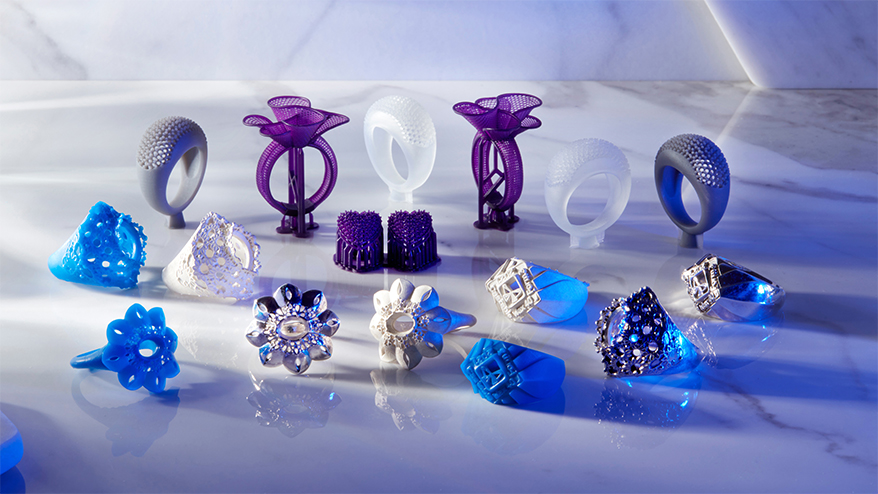
Types of 3D Printing Technologies Used in Jewelry
Several 3D printing technologies are utilized in jewelry production, each offering unique advantages and applications:
1. Stereolithography (SLA):
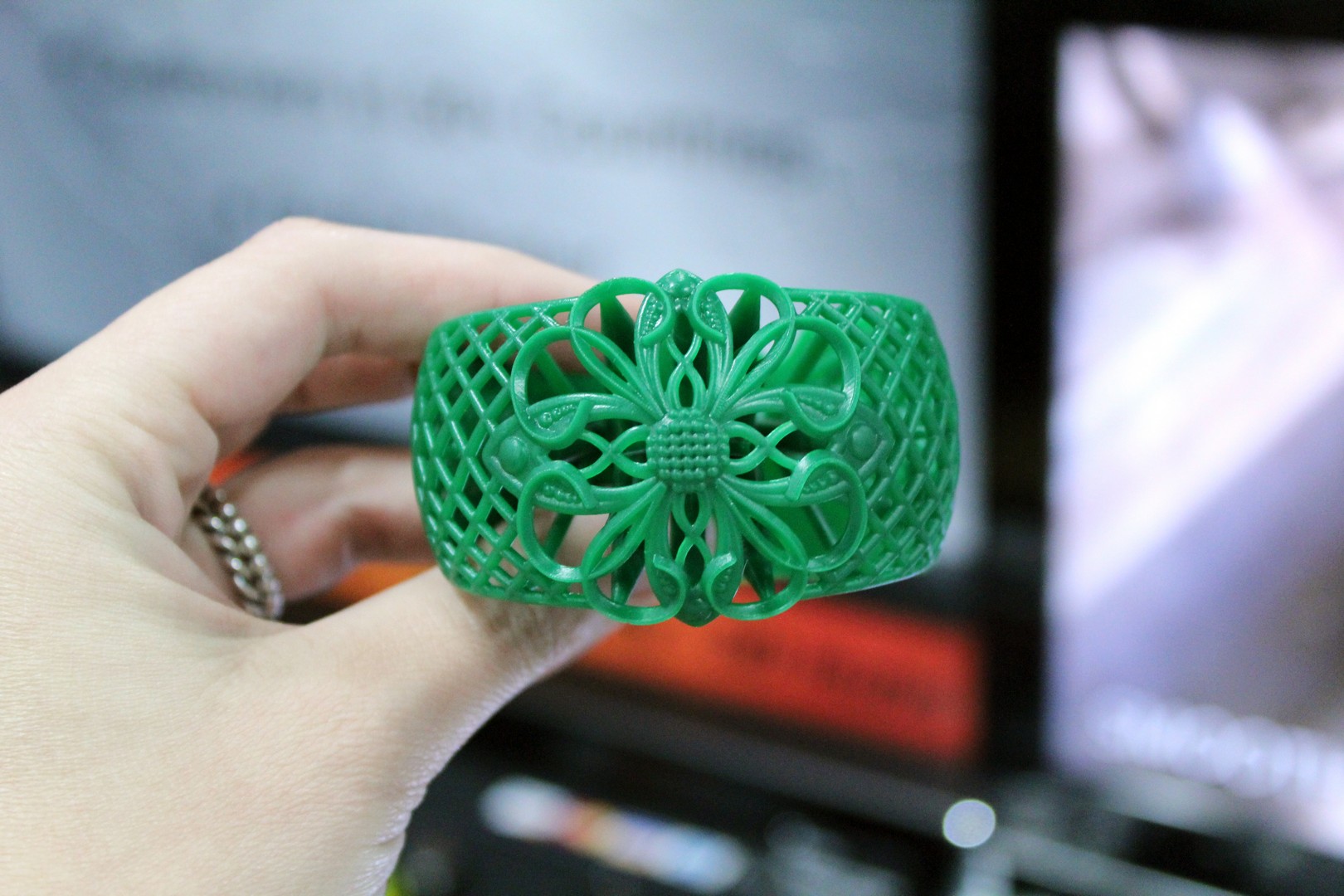
SLA is a widely used 3D printing technology for jewelry production. It involves using a UV laser to cure a liquid photopolymer resin, layer by layer, creating a solid object. SLA is known for its high resolution and excellent surface finish, making it ideal for producing intricate jewelry with fine details.
2. Selective Laser Sintering (SLS):
SLS uses a laser to fuse powdered materials, such as nylon, plastic, or metal, layer by layer. It is suitable for creating strong and durable jewelry pieces with complex geometries. SLS is particularly well-suited for producing large-scale jewelry pieces or pieces with intricate internal structures.
3. Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM):
FDM is a popular and cost-effective 3D printing technology. It involves extruding thermoplastic filament through a heated nozzle, layer by layer, to create a solid object. While FDM offers good resolution and versatility, it is generally less precise than SLA or SLS, making it more suitable for creating jewelry pieces with simpler designs.
4. Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS):
DMLS is a high-end 3D printing technology that uses a laser to fuse powdered metal, layer by layer, creating a solid metal object. DMLS is known for its exceptional strength, durability, and precision, making it ideal for producing high-quality jewelry pieces in precious metals like gold, silver, and platinum.
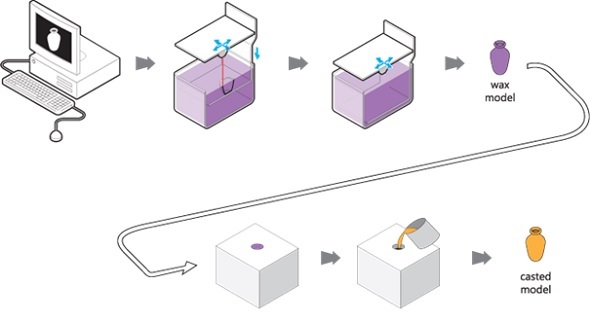
5. Lost Wax Casting:
While not a direct 3D printing method, lost wax casting is often used in conjunction with 3D printing to create jewelry pieces in precious metals. In this process, a 3D printed wax model is used to create a mold, which is then filled with molten metal. The wax model is burned away, leaving behind a finished metal piece. This method offers excellent detail and precision, making it suitable for producing intricate jewelry designs.
The Impact of 3D Printing on the Jewelry Industry: A Paradigm Shift
The adoption of 3D printing is transforming the jewelry industry in profound ways, creating new opportunities and challenges for designers, manufacturers, and consumers alike.
1. Emerging Business Models:
3D printing is driving the emergence of new business models in the jewelry industry. Online platforms and marketplaces are facilitating direct-to-consumer sales, allowing designers to connect with customers without the need for traditional intermediaries. This shift empowers independent designers and small businesses, fostering innovation and entrepreneurship.
2. Increased Customization and Mass Personalization:
The ability to personalize jewelry is becoming increasingly prevalent, thanks to 3D printing. Customers can now design their own jewelry, incorporating unique details and preferences, creating truly personalized pieces that reflect their individual style and identity. This trend is blurring the lines between mass production and bespoke design, creating a new era of personalized jewelry.
3. Sustainable and Ethical Production:
3D printing promotes sustainable and ethical jewelry production. The technology reduces material waste, minimizes energy consumption, and allows for on-demand production, reducing the need for large inventories and minimizing environmental impact. Additionally, 3D printing enables the use of recycled materials and the creation of jewelry with minimal ecological footprint.
4. Enhanced Customer Experience:
3D printing enhances the customer experience in the jewelry industry. Customers can engage with designers through virtual platforms, visualize their designs in 3D, and track the progress of their orders, creating a more transparent and interactive experience. This personalized and engaging approach fosters stronger customer relationships and builds brand loyalty.
5. New Design Possibilities and Artistic Expression:
3D printing empowers designers to push the boundaries of creativity and artistic expression. The technology enables the creation of intricate designs with complex geometries, organic shapes, and unconventional textures, opening up new possibilities for jewelry design. This creative freedom is fostering a renaissance in jewelry design, bringing forth innovative and captivating pieces.
FAQs on 3D Jewelry Printing: Addressing Common Questions
1. What are the materials used in 3D jewelry printing?
3D jewelry printing utilizes a wide range of materials, including:
- Resins: Photopolymer resins are commonly used in SLA printing for their detail and smooth finish.
- Plastics: Thermoplastics like nylon and ABS are used for durable and affordable jewelry pieces.
- Metals: Precious metals like gold, silver, and platinum can be used in 3D printing technologies like DMLS and lost wax casting.
- Wax: Wax is used for creating models in lost wax casting, where a wax model is used to create a mold for metal casting.
2. Is 3D printed jewelry durable?
The durability of 3D printed jewelry depends on the material used and the printing process. Jewelry printed with strong materials like metal or certain plastics can be highly durable and resistant to wear and tear. However, jewelry printed with softer materials may be more prone to scratches or damage.
3. How does 3D printed jewelry compare to traditionally made jewelry?
3D printed jewelry offers several advantages over traditionally made jewelry, including:
- Greater design freedom: 3D printing allows for more intricate and complex designs.
- Customization: 3D printing enables personalized jewelry with unique details.
- Faster production: 3D printing significantly reduces lead times.
- Reduced material waste: 3D printing minimizes material waste and environmental impact.
However, traditional jewelry making still offers advantages in certain areas, such as:
- Handcrafted quality: Traditional jewelry often has a unique handcrafted feel.
- Established techniques: Traditional techniques have been perfected over centuries.
- Availability of materials: Some materials may not yet be suitable for 3D printing.
4. Is 3D printed jewelry expensive?
The cost of 3D printed jewelry can vary depending on factors such as the material used, the complexity of the design, and the production volume. However, 3D printing can be a cost-effective solution for producing custom jewelry, especially in smaller batches.
5. Where can I find 3D printed jewelry?
3D printed jewelry is becoming increasingly available through various channels:
- Online marketplaces: Platforms like Etsy and Shopify host a wide selection of 3D printed jewelry.
- Independent designers: Many designers offer custom 3D printed jewelry through their websites and social media channels.
- Jewelry stores: Some jewelry stores are now carrying 3D printed jewelry alongside traditional pieces.
Tips for Choosing and Caring for 3D Printed Jewelry
1. Consider the Material:
The material used for 3D printed jewelry can significantly impact its durability and aesthetic appeal. Choose materials that are suitable for your desired style and wear.
2. Look for Quality Craftsmanship:
Just like with any jewelry, look for 3D printed pieces that are well-crafted and have a smooth finish. Avoid pieces with rough edges or uneven surfaces.
3. Understand the Care Instructions:
Different materials require different care. Be sure to understand the specific care instructions for your 3D printed jewelry to ensure its longevity.
4. Avoid Harsh Chemicals:
Avoid exposing 3D printed jewelry to harsh chemicals like bleach, perfumes, or cleaning solutions, as these can damage the material.
5. Store Properly:
Store your 3D printed jewelry in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight or heat.
Conclusion: The Future of Jewelry is 3D Printed
3D printing is transforming the jewelry industry, ushering in an era of innovation, customization, and sustainability. The technology empowers designers to create unique and intricate pieces, while providing consumers with a wider range of choices and personalized options. As 3D printing continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more groundbreaking designs and innovative applications in the jewelry industry, shaping the future of this timeless art form.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Rise of 3D Printing in Jewelry: A Revolution in Design and Production. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!