The Rise Of Precision: A Comprehensive Guide To 3D Jewelry Printing
The Rise of Precision: A Comprehensive Guide to 3D Jewelry Printing
Related Articles: The Rise of Precision: A Comprehensive Guide to 3D Jewelry Printing
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Rise of Precision: A Comprehensive Guide to 3D Jewelry Printing. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Rise of Precision: A Comprehensive Guide to 3D Jewelry Printing
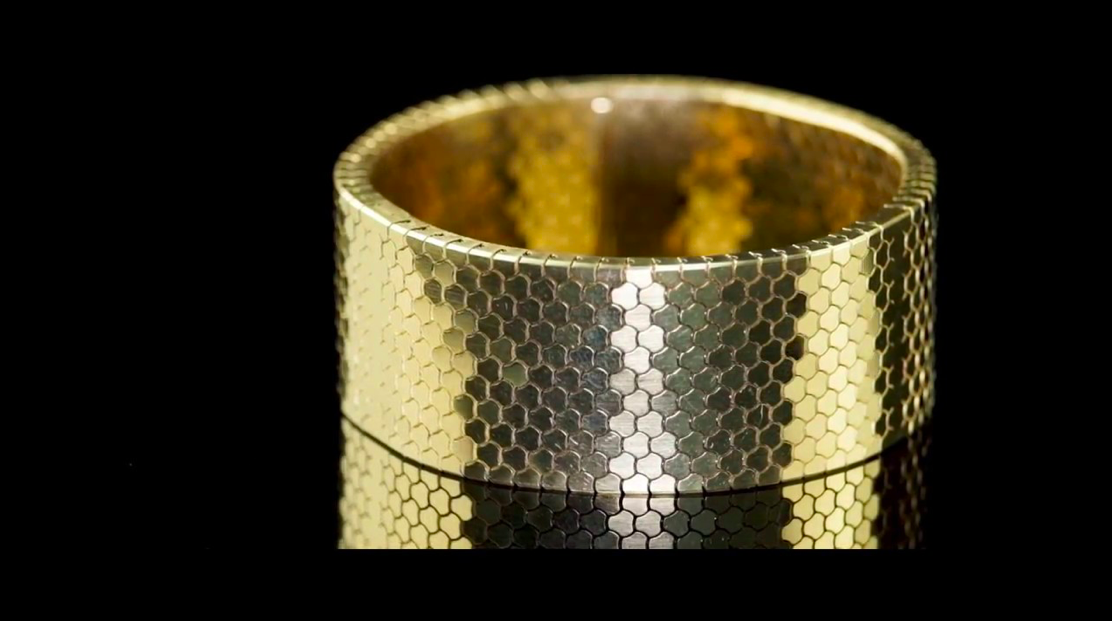

In the realm of jewelry creation, innovation is constantly pushing boundaries. Among the most transformative technologies to emerge in recent years is 3D jewelry printing. This advanced manufacturing process empowers jewelers and designers to translate their creative visions into tangible, intricate pieces with unparalleled precision and detail.
Understanding the Fundamentals of 3D Jewelry Printing
3D jewelry printing, also known as additive manufacturing, utilizes a layered approach to build jewelry pieces from digital designs. Unlike traditional methods like casting or hand-crafting, which often involve subtractive processes, 3D printing adds material layer by layer until the desired shape is achieved. This process offers a multitude of benefits, including:
1. Unparalleled Design Freedom:
3D printing liberates designers from the constraints of conventional jewelry-making techniques. Complex geometries, intricate patterns, and personalized designs become readily attainable, allowing for the creation of truly unique and bespoke pieces.
2. Enhanced Customization:
The ability to print on demand enables the creation of jewelry tailored to individual preferences. Customers can personalize their pieces with specific dimensions, engravings, or even incorporate their own designs, making each piece truly one-of-a-kind.
3. Reduced Material Waste:
3D printing utilizes only the necessary material for each design, resulting in minimal waste compared to traditional methods. This eco-conscious approach contributes to a more sustainable jewelry production process.
4. Prototyping Efficiency:
Rapid prototyping is a key advantage of 3D printing. Designers can quickly create multiple iterations of their designs, test different concepts, and refine their creations before committing to final production. This iterative process accelerates the design cycle and allows for faster market entry.
5. Cost-Effectiveness for Small-Scale Production:
While large-scale production might still favor traditional methods, 3D printing proves particularly cost-effective for small-scale production runs and custom orders. This makes it an ideal option for independent jewelers, designers, and small businesses seeking to create unique pieces without incurring high upfront costs.
Types of 3D Jewelry Printing Technologies:
Several 3D printing technologies are employed in jewelry creation, each offering distinct advantages and applications:
a. Stereolithography (SLA): This technology utilizes a UV-sensitive liquid resin that solidifies layer by layer when exposed to a UV laser beam. SLA is known for its high precision and smooth surface finishes, making it suitable for intricate and detailed jewelry designs.
b. Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): SLS uses a laser to fuse powdered materials, typically metal alloys or plastics, into a solid object. This technology is well-suited for complex designs and offers high strength and durability.
c. Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): FDM, also known as fused filament fabrication, extrudes a thermoplastic filament layer by layer, creating a three-dimensional object. While FDM offers lower precision compared to SLA or SLS, it is cost-effective and suitable for prototyping and less intricate designs.
d. Digital Light Processing (DLP): DLP utilizes a projector to cure a photopolymer resin layer by layer, similar to SLA. DLP offers faster printing speeds than SLA, making it suitable for larger production runs.
e. Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS): DMLS employs a high-powered laser to fuse metal powder, creating intricate and robust jewelry pieces. This technology is often used for high-end jewelry production and offers exceptional detail and durability.
Materials Used in 3D Jewelry Printing:
The choice of material is crucial in 3D jewelry printing, as it determines the final aesthetics, durability, and price of the piece. Some common materials used include:
a. Precious Metals: 3D printing allows for the creation of jewelry using precious metals like gold, silver, platinum, and palladium. This opens up possibilities for intricate designs and personalized pieces with a luxurious feel.
b. Resins: Photopolymer resins offer a wide range of colors, textures, and finishes. They are often used for prototyping and creating unique, affordable jewelry pieces.
c. Ceramics: 3D printing with ceramics enables the creation of jewelry with a distinct aesthetic and durability. This technology is particularly well-suited for intricate designs and fine details.
d. Plastics: Thermoplastics like ABS, PLA, and nylon are cost-effective options for jewelry prototyping and creating affordable pieces.
The Importance of Post-Processing:
After 3D printing, jewelry pieces often require post-processing to achieve the desired finish and properties. Common post-processing steps include:
a. Cleaning: Removing excess material and supports from the printed piece.
b. Sanding and Polishing: Smoothing the surface and achieving a desired sheen.
c. Finishing: Applying coatings or treatments for added durability, color, or texture.
d. Setting Stones: Incorporating gemstones into the design.
Benefits of 3D Jewelry Printing:
The adoption of 3D printing in the jewelry industry has brought forth a wave of benefits, revolutionizing the way jewelry is designed, manufactured, and experienced.
1. Enhanced Design Complexity:
3D printing allows for the creation of intricate and complex designs that would be impossible to achieve with traditional methods. This opens up new avenues for creativity and allows jewelers to explore previously uncharted design territories.
2. Personalized Jewelry:
3D printing empowers designers to create truly bespoke jewelry tailored to individual preferences. Customers can personalize their pieces with specific dimensions, engravings, or even incorporate their own designs, making each piece truly unique.
3. Reduced Lead Times:
3D printing significantly reduces lead times compared to traditional jewelry manufacturing processes. This enables jewelers to deliver custom pieces faster, meeting the growing demand for personalized and timely creations.
4. Increased Profitability:
The cost-effectiveness of 3D printing, particularly for small-scale production, allows jewelers to create unique pieces without incurring high upfront costs. This increased profitability enables them to explore new markets and offer competitive pricing.
5. Sustainable Production:
3D printing minimizes material waste compared to traditional methods, making it a more sustainable option for jewelry production. This eco-conscious approach aligns with growing consumer awareness of environmental responsibility.
6. Accessibility and Democratization:
3D printing democratizes jewelry creation, making it accessible to a wider audience, including independent designers, small businesses, and individuals with creative aspirations. This fosters innovation and empowers individuals to express their creativity through jewelry.
Challenges and Considerations:
While 3D jewelry printing offers numerous advantages, it also presents certain challenges and considerations:
1. Material Limitations:
The range of materials currently available for 3D jewelry printing is still limited compared to traditional methods. This can restrict design options and limit the availability of certain finishes and properties.
2. Scalability:
While 3D printing is cost-effective for small-scale production, scaling up production for large-scale orders can pose challenges. This requires careful planning and investment in specialized equipment and facilities.
3. Skill and Expertise:
Operating 3D printing equipment and mastering the design and post-processing techniques requires specialized skills and expertise. Training and ongoing education are crucial for jewelers and designers to fully leverage the potential of 3D printing.
4. Intellectual Property Protection:
The ease of replication and customization offered by 3D printing raises concerns about intellectual property protection. Designers need to implement robust measures to safeguard their designs and prevent unauthorized copying.
5. Cost of Equipment and Materials:
The initial investment in 3D printing equipment and materials can be significant, particularly for high-end technologies like DMLS. This can be a barrier to entry for small businesses and individuals.
FAQs about 3D Jewelry Printing:
Q: What are the most common materials used in 3D jewelry printing?
A: The most common materials used in 3D jewelry printing include precious metals (gold, silver, platinum, palladium), resins, ceramics, and plastics (ABS, PLA, nylon).
Q: How durable are 3D printed jewelry pieces?
A: The durability of 3D printed jewelry depends on the material used and the post-processing techniques applied. Precious metals offer high durability, while resins and plastics can be more susceptible to scratches and wear.
Q: Can 3D printed jewelry be set with gemstones?
A: Yes, 3D printed jewelry can be set with gemstones. The process involves creating a setting during the printing process or incorporating a separate setting after printing.
Q: Is 3D jewelry printing a sustainable option?
A: Yes, 3D printing is considered a more sustainable option than traditional jewelry manufacturing methods due to its reduced material waste and ability to create on-demand pieces.
Q: What are the advantages of 3D jewelry printing over traditional methods?
A: 3D jewelry printing offers advantages such as enhanced design complexity, personalization, reduced lead times, increased profitability, and sustainable production.
Q: What are the limitations of 3D jewelry printing?
A: Limitations of 3D jewelry printing include material limitations, scalability challenges, the need for specialized skills, intellectual property protection concerns, and the cost of equipment and materials.
Tips for Jewelers and Designers Considering 3D Jewelry Printing:
1. Research and Choose the Right Technology:
Thoroughly research different 3D printing technologies to determine the best fit for your specific needs and design requirements.
2. Invest in Quality Materials:
Select high-quality materials that meet your design specifications and durability requirements.
3. Master Post-Processing Techniques:
Develop expertise in post-processing techniques to achieve the desired finish and properties for your jewelry pieces.
4. Partner with Experienced Professionals:
Consider collaborating with experienced 3D printing service providers or manufacturers to ensure high-quality results and efficient production.
5. Stay Updated on Industry Trends:
Keep abreast of the latest advancements in 3D printing technology, materials, and design software.
Conclusion:
3D jewelry printing has emerged as a transformative technology in the jewelry industry, offering unparalleled design freedom, enhanced customization, reduced lead times, increased profitability, and a more sustainable approach to production. While challenges exist, the benefits of 3D printing far outweigh the limitations, paving the way for a future where jewelry is more personalized, innovative, and accessible than ever before. As technology continues to advance, 3D jewelry printing will undoubtedly play an increasingly vital role in shaping the future of jewelry design and creation.
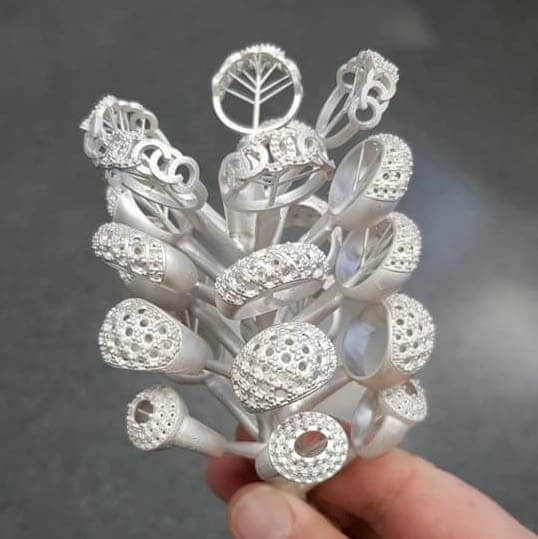






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Rise of Precision: A Comprehensive Guide to 3D Jewelry Printing. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!